With the rapid growth of railway mileage in China, the degree of heavy load of railway wagons continues to increase. An interference technology based on Rayleigh backscattering signal in optical fiber was proposed by using existing communication optical cables along railway lines. When the fiber vibrated slightly, the phase and refractive index of the fiber at disturbed position changed, which resulting in the Rayleigh backscattering light. By performing differential calculation on the Rayleigh signal curves before and after the operation, the location of the interference light intensity signal corresponded to the location of the disturbances was obtained. Based on this method, the recognition and positioning of railway vehicles were realized. By collecting and analyzing the time-domain and frequency-domain signal, the signal strength, train length, the number of carriages and other characteristics were extracted, and the model of railway vehicles were accurately recognized. Compared with traditional positioning technologies, this technology could realize long-distance monitoring, and the sensing fiber was buried underground on both sides of the railway, which was conducive to the concealment and protection of optical fiber. Experimental results show that the positioning error of the system is within ±10 m, and the detection of railway speed and position within 25 km can be realized.
The downlink single input multiple output (SIMO) and uplink multiple input single output (MISO) technologies of laser communication of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) air-ground slant in atmospheric turbulence channel were studied. Based on the atmospheric turbulence model of Gamma-Gamma distribution, the Meijer function was used to derive the bit error rate (BER) closed expression of SIMO technology in downlink under the combined influence of atmospheric turbulence and pointing error. An approximate expression of BER performance of MISO technology in uplink of Gamma-Gamma turbulence model was established based on α-μ distribution. The effects of antenna number, zenith angle and pointing error on the system were studied systematically. The results show that the spatial diversity technology can effectively improve the BER performance of the system. When the beam divergence angle is 500 μrad, and the downlink receiver as well as the uplink transmitter are 3, the performance optimization can be over 10 dB. The zenith angle has a significant influence on the BER performance of air-ground slant laser communication. In order to meet the performance requirement of 10-6 of system BER, the zenith angle should be controlled within a small range of about 30 degrees.
The high birefringent microstructured optical fiber (MOF) with small defective holes in fiber core and elliptical cladding air holes was designed for polarization-maintaining waveguide transmission for terahertz wave. By selectively filling the terahertz epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) materials in cladding air holes, the dual asymmetry of the geometric structure and the material distribution was introduced, and the degeneracy of two polarized fundamental modes was broken to obtain the high birefringence. The variation of transmission properties such as birefringence, loss and dispersion with structural parameters was studied by finite element method (FEM). In the wide-band range from 0.5 THz~2 THz, the high birefringence greater than 0.01 was obtained. The loss of the x-polarized and y-polarized fundamental mode has the minimum value around 0.8 THz, which are 0.903 dB·cm-1 and 0.851 dB·cm-1, respectively. The dispersion characteristics can be effctively adjusted by the defective holes in fiber core, and the y-polarized fundamental mode has the near-zero flattened dispersion characteristics of (0±0.054) ps·THz-1·cm-1 in the range of 1 THz~1.8 THz. The transmission characteristics of the designed fiber are insensitive to the refractive index changes of ENZ material. The research conclusions provide theoretical references for the development of terahertz polarization maintaining fiber.
Based on the theoretical model of Erbium-ytterbium doped fiber amplifier (EYDFA) and the analysis theory of stimulated Raman scattering effect, a hybrid amplifier structure combining EYDFA with second-order multi pump Raman fiber amplifier (RFA) was studied and designed by using the gain spectrum complementary characteristics of EYDFA and RFA. In order to obtain a hybrid amplifier with high gain and low flatness, a particle swarm optimization algorithm was introduced to optimize the pump wavelength and power. The simulation results show that, without the use of gain equalizer, the output power of the designed hybrid fiber amplifier is approximately equal, the average gain is 38.78 dB and the gain flatness is 1.1 dB in the bandwidth range of 90 nm, which provides a reference for the design and optimization of the hybrid amplifier.
The circumferential stress caused by blood flow in blood vessels is closely related to the structural and functional changes of blood vessels. Measuring the circumferential stress of blood vessel models in vitro is an important issue in biomechanics research. A method for measuring the circumferential stress of blood vessels by using fiber gratings was proposed, and a three-dimensional circular blood vessel model integrating fiber gratings was established by using steel needle mold based on microfluidic technology. The relationship between different flow velocities and stress was studied through simulation. The simulation results show that the stress changes linearly with the flow velocity in the range of 8 mm/s~75 mm/s. The circumferential stress generated by fluid flow was measured by fiber Bragg grating sensor. According to the experiment, the relationship between wavelength change of grating and velocity was obtained. When the flow velocity range varies from 8 mm/s to 75 mm/s, the wavelength change caused by velocity is 0.173 nm. The relationship between stress and wavelength change of grating was obtained by simulation experiment. A microfluidic blood vessel model with fiber Bragg grating sensor was proposed and implemented, which provides a new idea for measuring circumferential stress in vitro when blood flows.
To improve the stability and portability of the sensor, a refractive index sensor based on hollow micro-bottle resonator was proposed to package the system and study its refractive index sensing properties. The optical field distribution of radial echo-wall mode of hollow micro-bottle resonator under different wall thicknesses was simulated and analyzed. The proportion of the optical field inside the micro-bottle increased with the decrease of wall thickness of device, which was beneficial to improve the sensing sensitivity. To reduce the wall thickness, the quartz capillary was etched by hydrofluoric acid, which was used to fabricate the thin-wall hollow micro-bottle resonator by fusion splicer. The coupling system was packaged and fixed on a slide by using UV adhesive, which enhanced the stability and portability of the sensor. Finally, the sensing characteristics of the packaged device under different refractive index matching fluids were studied and the sensing sensitivity was 26.50 nm/RIU. The proposed sensor has the advantages of high stability, high flexibility and low loss, which has great application potential in optofluidic refractive index detection.
A high-sensitivity temperature sensor based on dual-core fiber coupling effect and vernier effect was proposed. The sensor was composed of two fibers which with a certain length difference, they were dual-core photonic crystal fiber and single mode fiber. The vernier effect was achieved by dual-core photonic crystal fiber through the cascade, and in the meantime the temperature sensing was achieved by filling the pores with ethanol in the middle of the fiber core. The simulation results show that the average temperature sensitivity of -20.37 nm/℃ of the temperature sensor can be achieved in the temperature range of 35℃~45℃. Compared with the sensor which only depends on the energy coupling effect of dual-core photonic crystal fiber, the temperature detection sensitivity of the proposed sensor is 10 times higher.
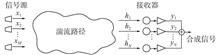
The influence of atmospheric turbulence on wireless optical communication systems cannot be ignored. In order to accurately reflect the actual features of laboratory-simulated multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) atmospheric turbulence channels, a method using phase screens to simulate MIMO atmospheric turbulence channels was proposed. The liquid crystal modulation method based on liquid crystal spatial light modulator (LC-SLM) was studied, and the feasibility of the method was verified by experiments. The experimental results show that the laser spot of MIMO atmospheric turbulence channels simulated by phase screen has different degrees of distortion. In the turbulent environment, the power stability of the two-channel laser emission system is better than that of the single-channel laser emission system. Under the forward error correction error limit (3.8×10-3), the link penalty of the single-emission single-receiving system is 10.5 dB, and the link penalty of the two-emission two-receiving MIMO system is 9.3 dB. This research provides a new idea for the experimental method of simulating MIMO atmospheric turbulent channels in laboratory.
In order to meet the demand of microseismic monitoring in oil and gas development, a new type of underground three components optical fiber microseismic monitoring system was designed based on time-division multiplexing scheme. Combined with indoor test, the background noise of the system was less than -101 dB, dynamic range more than 120 dB, interstage crosstalk less than -67 dB, which meet the needs of microseismic signal detection. The system was successfully applied to the field detection of hydraulic fracturing microseism in Xinjiang Oilfield. The monitoring results show that the system can clearly capture the P-wave and S-wave signals of microseism, better reveal the characteristic information of hydraulic fracturing microseismic signals, and establish a good foundation for the spatial location of microseismic events and the interpretation of fracture characteristic parameters.
A temperature sensor based on coreless-few mode-coreless optical fiber structure was proposed for theoretical analysis and experimental study. The coreless fiber (CLF) and the few-mode fiber (FMF) were fused together to form a coreless-few mode-coreless optical fiber structure, and the single-mode fiber (SMF) was fused at both ends of the structure as input and output fiber. The mode mismatch between the first section of coreless fiber and single-mode fiber could excite higher-order modes. The two modes of LP01 and LP11 in the few-mode fiber were transmitted along the core of the few-mode fiber. Under the action of the second section coreless fiber, the two modes were recoupled back to the single-mode fiber, and the two modes interfered to form an interference spectrum. When the outside temperature changed, the optical path difference between the two modes also changed, and the interference troughs of the interference spectrum were shifted. Two different interference troughs were selected as the characteristic wavelengths for experimental analysis. The experimental results show that the interference troughs with wavelength around 1 550 nm and 1 534 nm both have red shift, and the corresponding temperature sensitivity is 68 pm/ and 44.5 pm/ respectively. The sensing structure has the advantages of simple fabrication, high sensitivity and good application prospects.
The demodulation method of fiber Bragg gratings (FBG) based on long-period fiber gratings (LPFG) was studied. The transmission spectrum of LPFG was used as the edge filter to demodulate the FBG, and the demodulation performance mainly depended on the transmission spectrum depth of LPFG. The influence of CO2 laser writing technique on the transmission spectrum was analyzed in detail, and the LPFG with transmission spectrum depth of 25 dB was manufactured and used as the FBG demodulation device. The demodulation system was built with the FBG pasted on the surface of the metal strain sheet. The static and dynamic response of the sensing system was tested. The experimental results show that the proposed method has the advantages of simple production process, low cost, good linear dynamic range and higher sensitivity.
To test whether the fiber Bragg grating (FBG) sensor can endure the steady-state inertial loads caused by the acceleration and the sensing properties during the loads, a FBG strain and temperature sensor with aluminium alloy substrate package was designed, and the acceleration performance on the sensor was tested. The sizes of FBG strain and temperature sensor were designed and its package process was described. The strain and temperature sensing mechanisms of FBG sensor were analyzed, and the spectrum detection and demodulation system based on volume phase grating and linear array photodetector was developed. Finally, the acceleration test equipment was established, and the acceleration performance test of the selected FBG strain and temperature sensor was carried out in accordance with the requirements and methods of GJB150.15A acceleration test. The experimental results show that in the 2 min performance test before and after the acceleration test, the wavelength offset is below to ±50 pm, and the change of light intensity is below to 0.3 V. In acceleration test, the maximum fluctuation of wavelength offset is ±7 pm, and the light intensity is in the range of 1.3 V~4.003 V. It is proved that the designed FBG sensor has the ability to endure the acceleration loads and has the good sensing performance during the acceleration loads.
A distributed optical fiber temperature measurement system with a high spatial resolution was designed to overcome the shortcomings of the existing vertical profile temperature measurement technology for winter ice cover. The measurement principle and overall structure of the system were introduced, and the deconvolution correction algorithm was proposed to avoid the inaccurate temperature measurement caused by the limited bandwidth of the system, thereby enhancing the spatial resolution. At the same time, the relevant temperature measurement experiments were carried out. The algorithm could improve the spatial resolution of the system from 1.3 m to 0.5 m under the premise of ensuring the accuracy of temperature measurement. On this basis, a temperature measurement device with a high vertical resolution was designed, which could accurately detect the temperature change in the vertical direction of the ice cover to achieve the purpose of identifying the thickness of the ice cover.
The fiber grating sensor has the advantages of light weight, small size, high sensitivity, strong anti-electromagnetic interference capability and so on, especially good flexibility and compatibility. The fiber grating and flexible materials can be fabricated into a flexible sensor with high-density distributed perception by means of the special preparation technology. The basic sensing principles of fiber grating were introduced; then the fiber grating flexible sensors using silicone rubber, textile and other polymers as the substrates were introduced in detail, and the preparation technologies, structural characteristics and performance of various flexible sensors were analyzed; finally, the main problems, application fields and future research directions of flexible sensors were discussed.
The coupling mechanism and temperature sensing characteristics based on the micro-sphere resonant cavity coupled apparatus embedded in capillary were investigated. The micro-sphere support the high-order modes, which is easy to meet the phase matching condition with the modes in the quartz capillary, thus the mode of micro-sphere echo wall will be excited. The temperature sensing of a barium titanate micro-sphere was tested. A polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) micro-sphere was adopted to carry out the temperature sensing experiment for further enhancing the sensing sensitivity. The experimental results show that the temperature sensing sensitivity of PMMA micro-sphere can reach to 83.9 pm/℃, about eight times of that by the barium titanate micro-sphere, which plays an important role for improving the temperature sensing sensitivity.
The traditional fiber grating sensors are cross-sensitive to temperature stress and cannot simultaneously measure the change of the temperature stress of the measured object. In view of this situation, a new method of lithographing phase-shifted gratings using ultraviolet light was proposed. Before lithographing the gratings, the method of electrode discharge was used to remove the photosensitivity of a very small section of the optical fiber, so that the original uniform periodic distribution of the fiber was destroyed to form a phase-shifted grating, and its theoretical analysis was carried out. There were two distinct resonance peaks in the transmission spectrum of this phase-shifted grating. Using the properties of two peaks with different sensitivity to temperature and dependent variable, the simultaneous measurement of temperature and stress could be achieved by establishing the demodulation matrix. The experimental results show that the phase-shifted Bragg grating made by this method can realize the simultaneous measurement of temperature and stress accurately. The maximum temperature sensitivity of the sensor can reach to 9.51 pm/℃, and the sensitivity variance is lower than 2.125×10-7. The maximum strain sensitivity can reach to 0.767 pm/με, and the sensitivity variance is lower than 2.156×10-10.
A multi-wavelength thulium-doped actively mode-locked fiber laser was introduced, in which the gain medium was a 2 m thulium-doped fiber, and the active mode-locking could be realized by LiNbO3 intensity modulator. An optical filter based on birefringence was added into cavity, the birefringence filter effect of polarization maintaining fiber was used to filter out the superfluous supermode noise in cavity, and also the multi-wavelength output could be realized. The mode-locked pulse frequency spectrum signal-to-noise ratio could reach to 68.48 dB at fundamental frequency, and the maximum number of wavelength channels was 5 in a stable mode-locked state. Furthermore, the polarization independent isolator in cavity was replaced by polarization dependent isolator, and mode-locked pulse was modulated by digital signal. The optical signal-to-noise ratio of eye diagram can be increased by 8.67 dB, which indicates that time stability of mode-locked pulse can be improved effectively.